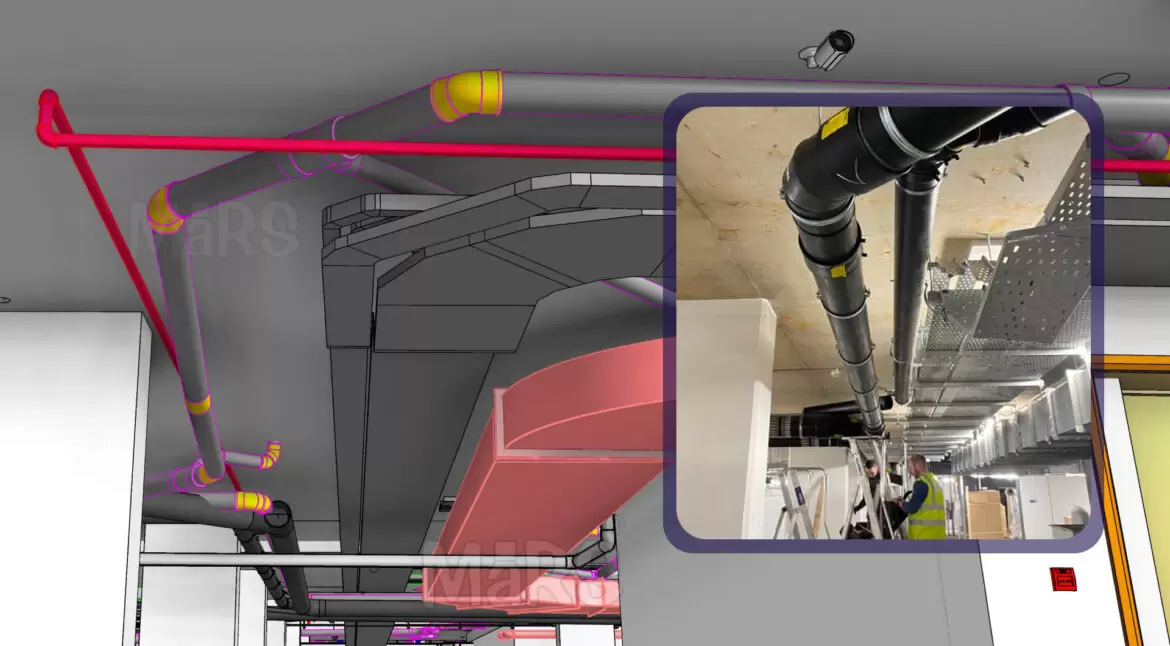
The MEP, which stands for Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing, refers to the important components that support a structure’s comfort and functionality in the complex building construction area. These systems are not just supporting elements but essential to the efficiency, safety, and proper functioning of any structure.
A suitable interior environment is maintained by mechanical systems that control the HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning). The power distribution, lighting, and communication networks that keep modern buildings linked and operational are all managed by electrical systems. Plumbing systems maintain hygienic conditions by managing waste, drainage, and water supply.
Everyone working in the design, planning, or management of construction projects requires a solid understanding of MEP in the construction i. This guide covers MEP services and systems’ components, their roles, and the precise way in which they are connected and developed for sustainable and efficient buildings. Understanding MEP basics is essential for anyone who is involved in construction, whether they are a building owner, project manager, or other role in the industry.
What is MEP in Construction?
Building sustainability, efficiency, and functionality are all dependent on integrated systems, which are referred to as MEP in the construction industry. These systems include plumbing, electrical, and mechanical (heating, ventilation, air conditioning, lighting, and communication), draining, sewage, and power distribution in the case of the latter three. For buildings to be operationally effective, secure and comfortable for their residents, an in-depth understanding of MEP is required.
Mechanical Systems in Building Construction
In buildings, mechanical systems are essential for preserving indoor temperature and air quality regardless of the outside weather. HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems are made to control these three elements, each of which has a specific role in maintaining a building’s temperature and general operation.
Heating Systems

Heating systems are responsible for maintaining indoor temperatures during cold weather, ensuring a warm and comfortable environment. Many types of heating systems are frequently used:
- Boilers: Boilers are central to many heating systems. They heat water to create hot water or steam, which is then pumped through underfloor heating systems or radiators. Boilers can be powered by various fuels, including natural gas, oil, or electricity.
- Heat Pumps: Heat pumps are versatile machines that move heat from one area to another. To heat a structure, they can absorb heat from the ground, the air, or the water. In addition to heating, heat pumps can also function as air conditioners by reversing the heat transfer process.
- Furnaces: Burning fuel (such as natural gas, oil, or propane) in a furnace produces heat, which is eventually distributed throughout the structure by ducts. They frequently work in combination with central air conditioning systems.
Energy-efficient design minimizes operating expenses and a building’s environmental effect, which is an advantage of effective heating systems. For maximum efficiency and comfort, modern heating systems frequently include advanced controls and zoning features.
Related blog: Why did contractors require MEP BIM for a construction project?
Ventilation Systems
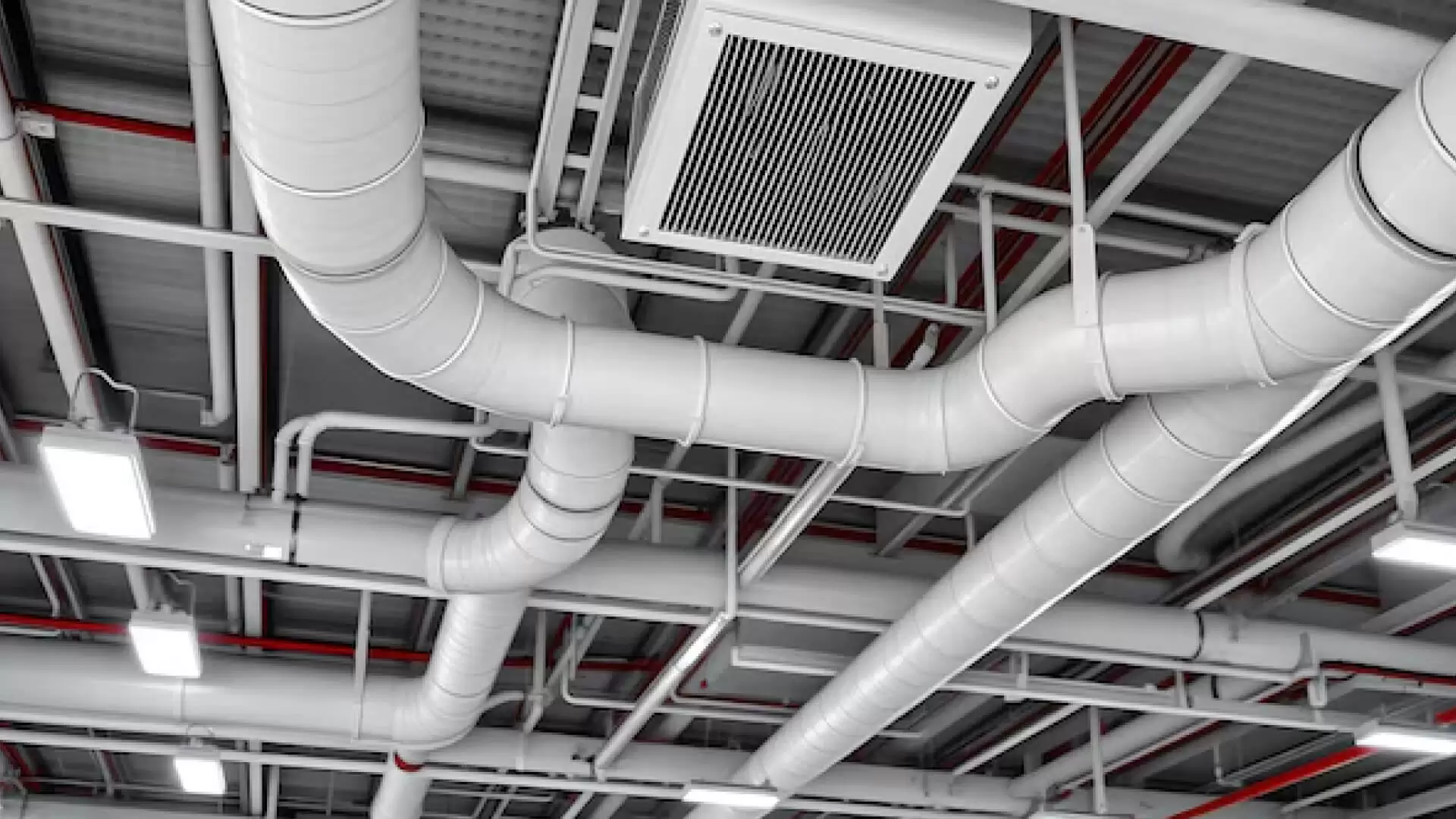

The continual supply of fresh air that ventilation systems provide to the inside environment is essential for preserving air quality while preventing the accumulation of stale, contaminated air. Having enough ventilation facilitates:
- Dilute Indoor Pollutants: Ventilation systems help to remove indoor pollutants such as carbon dioxide, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter. This is essential for maintaining healthy indoor air quality.
- Control Humidity: Ventilation systems assist in preventing problems caused by high humidity, like mold growth and degradation of building components, by eliminating surplus moisture from the air.
- Enhance Comfort: Sufficient ventilation guarantees that rooms don’t seem overly stuffy or drafty, which enhances overall comfort.
Types of ventilation systems include:
- Mechanical Ventilation: To actively circulate air throughout the building, fans and ducts are used in this process. Balanced ventilation systems, exhaust fans, and supply fans are a few examples.
- Natural Ventilation: To supply fresh air, this depends on natural circulation through windows, vents, and openings. It can be useful in moderate climates even if it is less manageable than mechanical ventilation.
- Hybrid Systems: Combining mechanical and natural ventilation, hybrid systems can adjust the amount of mechanical ventilation based on outdoor conditions and indoor air quality needs.
Air Conditioning Systems

Air conditioning systems are designed to cool and dehumidify indoor air, making indoor environments more comfortable during hot weather. Key components and types include:
- Central Air Conditioning: This system cools the air in the building by using a system of ducts. Throughout the year climate control, central air conditioning, and heating systems are frequently combined.
- Split Systems: There is an inside unit and an outdoor unit in a split air conditioning system. The compressor and evaporator are located outside the outdoor unit, and the evaporator coil is located within. Smaller rooms or areas are common places for this kind of setup.
- Packaged Systems: The compressor, condenser, and evaporator of a packaged air conditioning system are all contained in a single unit that is frequently placed on the building’s roof. These systems are frequently seen in business buildings.
- Ductless Mini-Split Systems: These systems do not require ductwork to supply heating and cooling. They allow for targeted climate management in various places by connecting an outside unit to one or more indoor units.
Air conditioning systems often feature advanced controls, such as programmable thermostats and smart sensors, to enhance energy efficiency and maintain consistent indoor conditions.
Electrical Systems

Electrical systems are integral to the daily operation of any building. They encompass:
Power Distribution
Power distribution is a critical aspect of electrical systems, ensuring that electrical energy is efficiently delivered from the power source to various parts of a building. This process involves several key components:
- Electrical Panels (Breaker Panels): The distribution of electrical circuits throughout the building is done through these central hubs. The circuit breakers or fuses in panels guard against overloads and short circuits.
- Circuit Wiring: Electricity from the panels is transferred via wiring to switches, outlets, and appliances. A safe and dependable electrical distribution system requires proper wiring.
- Transformers: In some cases, transformers adjust the voltage levels to ensure that power is suitable for use by different systems and appliances.
- Busbars: These are metal bars that conduct electricity within panels, helping to distribute power to various circuits efficiently.
The building’s overall energy consumption and safety are impacted by the power distribution system’s efficiency. To avoid problems like electrical overloads, which can cause outages or even fires, proper design and maintenance are essential.
Lighting Systems

Lighting systems are made to light up areas both inside and outside to a sufficient level. Good lighting improves a building’s appearance, safety, and visibility. Important elements consist of:
- Interior Lighting: This encompasses various types of fixtures such as ceiling lights, recessed lighting, chandeliers, and task lighting. The design of interior lighting should consider factors like the purpose of each room, ambient light levels, and energy efficiency.
- Exterior Lighting: Streetlights, floodlights, and landscape lighting are examples of exterior lighting. It improves the building’s beauty while also providing security and safety.
- Control Systems: Adjustable lighting levels and schedules are made possible by lighting control systems, which include controls, timers, and smart controls. These devices can adjust lighting according to various requirements and preferences while also increasing energy efficiency.
- Energy-Efficient Technologies: LED technology is widely used in modern lighting solutions because it is more energy-efficient and has a longer lifespan than conventional electric bulbs.
All regions of the building should have sufficient lighting based on their needs and usage, which means that lighting design must find a balance between energy economy, practicality, and aesthetics.
Communication Systems

For different building functions to operate and be connected, communication networks are necessary. Among them are:
- Telephone Systems: Voice communication within and outside the building is made possible using VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) systems or traditional landline systems.
- Data Networks: These involve computer networks, internet connectivity, and other data services supported by structured cabling systems. For dependable and fast data transfer, network infrastructure must be installed and maintained properly.
- Security Systems: Security communication systems include surveillance cameras, intercoms, and alarm systems. These systems monitor and protect the building from unauthorized access, theft, and other security threats.
- Public Address Systems: These are used for announcements and emergency notifications throughout the building. They are particularly important in large or complex buildings where clear communication is essential for safety and coordination.
Effective communication systems enhance the functionality and safety of a building by ensuring reliable connectivity, monitoring, and information dissemination.
Plumbing Systems

Plumbing systems are essential to a building’s infrastructure because they effectively manage waste disposal and water supply. These systems are made to guarantee efficient garbage removal and safe water delivery. Let’s analyze each element one by one:
1. Water Supply
The water supply system provides clean, drinkable water to all areas of a building. This is essential for drinking, cooking, sanitation, and other daily activities.
Components:
- Water Source: It might be a private well or a public supply. Regular testing and maintenance are necessary for private wells, but municipal supplies are usually treated and quality-monitored.
- Piping: Water is moved by a network of pipes made from copper, PEX (cross-linked polyethylene), or PVC (polyvinyl chloride). Temperature, pressure, and water quality are some of the variables that affect material choice.
- Pressure Regulation: The proper pressure of water is supplied throughout the structure according to pressure regulators and boosters. Maintaining appropriate pressure levels is essential to avoiding damage to fixtures and pipelines.
- Valves and Fixtures: Control over the water supply to particular places or appliances is made possible by shut-off valves. Water is accessed as needed by fixtures like sinks, toilets, and faucets.
Considerations:
- Water Quality: Filtration systems may be installed to remove impurities and ensure the safety of the water supply.
- Pipe Insulation: Insulating pipes lowers energy loss and helps keep them from freezing in cold areas.
2. Drainage
Wastewater from showers, sinks, and other fixtures is removed under the control of the drainage system. Blockages are avoided and waste is properly directed away from concentrating areas with the help of effective drainage.
Components:
- Drain Pipes: Wastewater from fixtures is transported by these pipes to the tank or drainage system. Typically, PVC, ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene), or cast iron are used to make them.
- Traps: U-shaped pipe sections that are placed under sinks and other appliances. Traps collect trash that may block pipes and stop sewer gasses from entering the building.
- Cleanouts: Access points along the drainage system that allow for the removal of blockages and maintenance.
- Ventilation: Vent pipes allow air to enter the drainage system, ensuring smooth flow and preventing vacuum conditions that could hinder drainage.
Considerations:
- Slope: To enable gravity-driven drainage, pipes need to be constructed with the appropriate slope. Generally, a slope of 1/4 inch per foot is advised.
- Maintenance: Maintaining system performance and preventing obstacles are made easier with regular drain cleaning and inspection.
3. Sewage
The treatment and disposal of waste from toilets and other hygiene fixtures is handled by the sewage system. Maintaining cleanliness and avoiding pollution requires effective sewage management.
Components:
- Sewer Lines: Large-diameter pipes that connect the building’s sewage to a septic tank or the city sewer system. Typically, PVC, clay, or concrete are used to make these.
- Septic Tanks: In areas without access to municipal sewers, septic tanks collect and treat sewage on-site. They separate solids from liquids and allow for bacterial digestion of waste.
- Pumps: In some systems, pumps are used to move sewage to higher elevations or through long distances where gravity alone is insufficient.
- Treatment Facilities: Treatment facilities for septic-system buildings could include leach fields or drain fields, where the treated wastewater is absorbed into the ground.
Considerations:
- System Capacity: The capacity of the sewage system must be adequate to handle the volume of waste generated by the building.
- Inspection and Maintenance: Regular maintenance of septic systems and sewer lines helps prevent failures and ensures proper operation.
Related blog: The Role of BIM in MEP System Fault Detection and Diagnostics
MEP Design Services
For the integration of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems into building projects, MEP design services are essential. These services guarantee that all systems operate in synchronization to satisfy a building’s requirements for efficiency, safety, and functionality. For spaces to be comfortable, environmentally friendly, and operationally effective, this integration is essential.
Building mechanical system optimization is the main goal of mechanical design services, which are an essential component of MEP design services. To guarantee effective HVAC systems that complement the overall architecture of the building, this MEP planning process entails several crucial elements.
To choose the appropriate equipment, the process starts with comprehensive load calculations to determine specific heating and cooling requirements. The next step in MEP design is selecting suitable HVAC equipment, such as air conditioners, heat pumps, boilers, or chillers, based on compatibility and performance.
Energy recovery systems and improved ducting are two methods that designers use to reduce consumption and operating expenses. Energy efficiency is a crucial factor in their designs. To improve system performance and comfort, smart technology and advanced control systems are also included.
To put it simply, mechanical design services guarantee that HVAC systems are carefully integrated into the architecture of the building, creating a comfortable and energy-efficient interior space.
Electrical Design Services
The development and implementation of successful electrical systems in buildings are the main objectives of electrical design services, which cover a wide range of activities. Mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) design services for electrical systems include integrating the electrical components into the overall building design smoothly and efficiently.
Electrical designing, which includes extensive preparation and specification of electrical systems, is the first of these services. This covers the arrangement of lighting, power distribution, and communication system integration. When electrical systems are designed, it guarantees that they not only satisfy the building’s operating requirements but also comply with energy efficiency and safety criteria.
Electrical MEP design services strive to maximize the performance and dependability of electrical systems, hence improving the general usefulness and sustainability of the building, through careful consideration of load calculations, equipment selection, and circuit design.
Plumbing Design Services
For building projects to ensure that plumbing systems are installed effectively and efficiently, plumbing MEP design services are crucial. These services cover a wide range of plumbing design topics, such as creating detailed blueprints for sewage, drainage, and water supply systems.
Creating complex designs that work in collaboration with the building’s other mechanical, electrical, and architectural components is a key component of plumbing MEP design services. Water supply and waste management systems are maximized for both functionality and compliance with local standards and regulations when plumbing design is done well. This includes planning for upcoming maintenance requirements, choosing suitable fixtures, and building pipe networks.
Plumbing MEP design services assist avoid future problems, lower installation costs and improve the overall effectiveness of the building’s plumbing infrastructure by applying cutting-edge technologies and processes.
MEP Engineering Services
MEP engineering services encompass the application of specialized engineering principles to the design, analysis, and optimization of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems within a building. These services are crucial for ensuring that MEP systems function efficiently, effectively, and sustainably. The core aspects of MEP engineering services include:
System Integration
System Integration involves the coordination and harmonization of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems to ensure that they function cohesively. This process is critical for:
- Ensuring Compatibility: MEP systems have to be created with smooth compatibility in consideration. For instance, HVAC duct placement shouldn’t obstruct plumbing or electrical wiring. System conflicts are avoided and smooth operation is guaranteed by effective integration.
- Optimizing Performance: Integrated systems can be optimized for better performance. For instance, the integration of HVAC systems with building management systems (BMS) allows for real-time monitoring and adjustments to maintain optimal conditions and energy efficiency.
- Reducing Costs: Proper integration can minimize redundancies and reduce installation and operational costs. It also helps in identifying potential issues early in the design phase, preventing costly modifications during construction.
Related blog: What is the role of an MEP engineer in construction?
Performance Analysis
Performance Analysis involves evaluating the effectiveness of MEP systems to identify and address inefficiencies. This includes:
- System Evaluation: Engineers assess how well each system performs in terms of energy use, operational efficiency, and compliance with design specifications. This might involve the use of simulation software and performance monitoring tools.
- Troubleshooting: Identifying and rectifying issues such as inadequate heating, cooling, or lighting, and inefficiencies in water use or power distribution. Performance analysis helps in diagnosing problems and proposing solutions.
- Optimization: Based on the analysis, engineers can make recommendations for system adjustments or upgrades. This might include recalibrating HVAC systems, upgrading lighting to more energy-efficient options, or improving plumbing design to enhance water flow and reduce waste.
Sustainability Consulting
Sustainability Consulting focuses on incorporating green building practices and energy-efficient solutions into MEP system design. Key aspects include:
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing solutions that reduce energy consumption, such as high-efficiency HVAC systems, LED lighting, and advanced building controls. Energy modeling and analysis are often used to predict and enhance energy performance.
- Green Certifications: Assisting projects in achieving green building certifications like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) or BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method). This involves ensuring that MEP systems meet the criteria for these certifications.
- Sustainable Practices: Integrating practices such as water conservation techniques (e.g., low-flow fixtures and rainwater harvesting) and the use of sustainable materials. Engineers also consider the lifecycle impact of MEP systems, aiming to reduce their environmental footprint.
MEP Drafting Services
MEP drafting services are crucial in the construction and renovation of buildings, focusing on the creation of detailed technical drawings and schematics for mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems. These services are fundamental in ensuring that MEP systems are designed, installed, and maintained correctly.
1. Accurate Representation
Accurate representation in MEP drafting involves creating precise and detailed diagrams that serve as a blueprint for the construction and installation of building systems. This includes:
- Detailed Drawings: MEP draftsmen create detailed drawings that cover all mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems, including layouts, dimensions, and specifications. The exact locations of the pipes, wiring, ducts, and equipment are shown in these drawings.
- System Specifications: The drafts include detailed information on system components, such as HVAC units, electrical panels, lighting fixtures, and plumbing fixtures. This ensures that all components meet design requirements and performance standards.
- Error Prevention: By providing accurate and detailed diagrams, MEP drafting services help prevent errors during installation, which can lead to costly rework and delays.
2. Coordination
Coordination is a key aspect of MEP drafting services, ensuring that the mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems are integrated seamlessly with the building’s architectural and structural elements. This involves:
- Integration with Architectural Plans: MEP draftsmen work closely with architects to ensure that the MEP systems are integrated into the building’s overall design. This includes coordinating with architectural features like walls, ceilings, and floors to avoid conflicts and ensure proper placement of systems.
- Coordination with Structural Elements: MEP drafting services must also align with the building’s structural framework. This involves ensuring that ductwork, piping, and wiring do not interfere with structural elements such as beams and columns.
- Clash Detection: Advanced MEP drafting services use software tools to detect and resolve clashes between MEP systems and other building systems. This proactive approach minimizes conflicts and ensures a smoother construction process.
3. Documentation
Documentation provided by MEP drafting services is essential for the ongoing maintenance and modification of building systems. This includes:
- As-Built Drawings: After construction is completed, MEP draftsmen create as-built drawings that reflect the final installation of MEP systems. These drawings are crucial for future reference, repairs, and upgrades.
- Maintenance Manuals: Detailed documentation often includes maintenance manuals that provide instructions on the operation and upkeep of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems. This helps facility managers ensure that systems are maintained properly and operate efficiently.
- Modification Records: When changes are made to MEP systems, updated drawings, and documentation are provided to reflect these modifications. This ensures that all stakeholders have access to the most current information.
Conclusion
MEP services are fundamental to the construction and operation of modern buildings. By understanding the role of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems, as well as the importance of MEP design, engineering, and drafting services, stakeholders can ensure that buildings are efficient, sustainable, and comfortable.
In addition to improving a building’s functioning and safety, investing in high-quality MEP services also helps to improve environmental sustainability and long-term operational savings. Progress in the construction sector requires knowledge of the most recent developments in MEP systems and services, which is becoming increasingly important as technology advances.