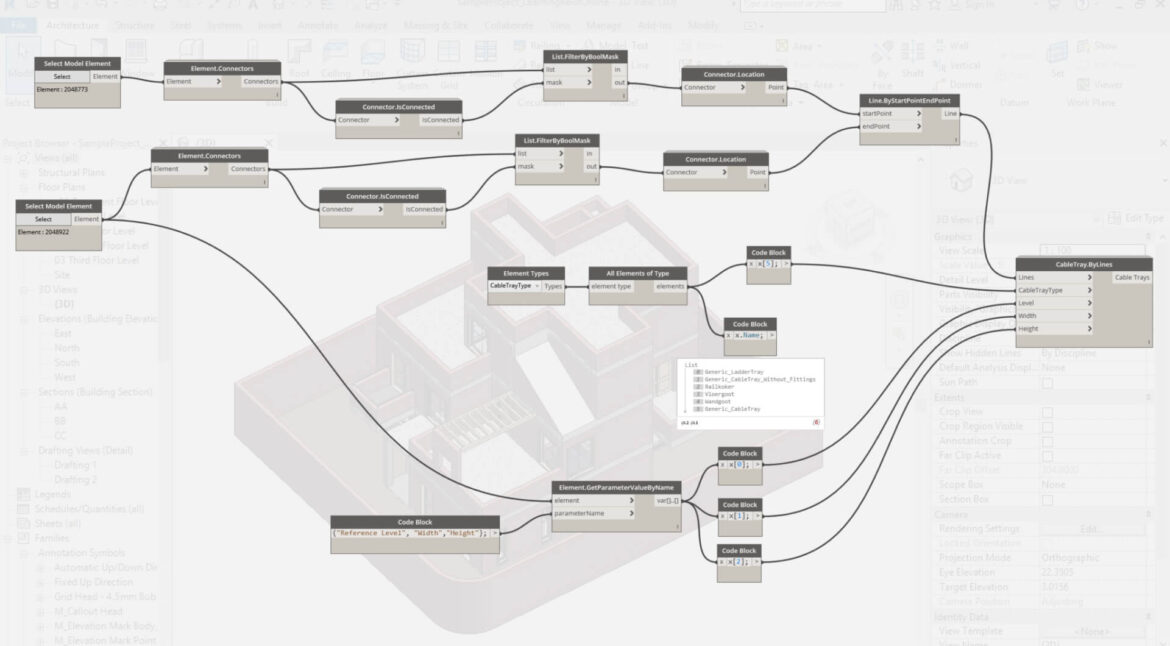
Building information modeling has transformed the construction industry, enabling teams to design, plan, and execute projects with unmatched precision. As the complexity of construction projects increases, manual processes can often lead to errors, inefficiencies, and inconsistencies in the model. This is where BIM automation is beneficial. Project teams can focus on important design and construction decisions, save time, and lower human error rates by automating repetitive and data-driven tasks. For automation to be implemented successfully, a systematic strategy is required to preserve the accuracy and dependability of the model. To ensure that automated workflows are executed perfectly and processes are simplified, a well-defined checklist for BIM automation is essential.
This blog post will discuss the BIM Automation Checklist, its importance, and how it can improve your process for BIM to deliver better project results. Whether automating parameter management, model documentation, or clash detection, having a BIM environment that is compliant, strong, and capable of handling the demands of complicated construction projects is ensured by following a checklist.
BIM Automation Checklist
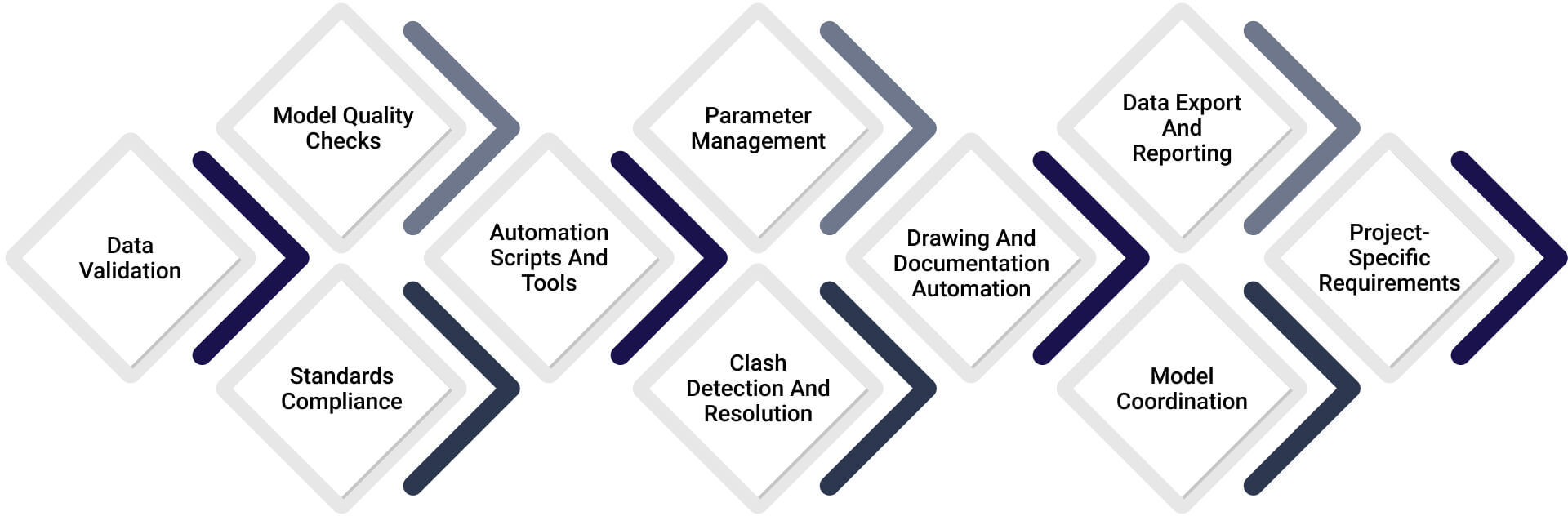
1. Data Validation
Verifying your data guarantees a reliable and steady base for your BIM model. It includes checking the completeness and accuracy of all input data, including files, naming standards, and parameter values. Make sure all element names, tags, and parameters adhere to the project’s naming guidelines while performing data validation. Running automation scripts with this step helps minimize errors and remove inconsistencies. For automated processes to operate efficiently and generate dependable results, a well-structured data format is essential.
2. Model Quality Checks
The 3D BIM model is checked for quality to make sure it meets the project’s requirements. To locate any connections, duplicate elements, or disconnected components, the geometry’s integrity must be checked. To ensure that it fulfills the planned work requirements, it also includes confirming the Level of Detail (LOD). Make sure that all of the elements are properly positioned, aligned, and free of gaps or misalignments during this stage. Accurate automation and downstream workflows depend on the model being maintained in good condition.
3. Standards Compliance
To preserve consistency throughout the BIM project, standards compliance is essential. For this, the model must be compared to relevant requirements like ISO 19650 or BIM guidelines unique to the company. Verify if naming conventions, families, templates, and modeling techniques all follow these guidelines. Rework and miscommunication may result from noncompliance. You can promote easier collaboration, more transparent communication, and trustworthy data sharing amongst stakeholders by guaranteeing compliance early on.
4. Automation Scripts and Tools
It’s crucial to verify the functionality of all scripts and tools before implementing BIM automation. Make sure there are no errors or unexpected outputs from the scripts and that they generate the desired results. Verify that every automation tool is current and works with the BIM environment as it is now. This step guarantees smooth execution and helps prevent interruptions during automated tasks. Frequent testing and updates increase the automation process’s reliability as well as effectiveness by avoiding problems that may occur from outdated programs.
5. Parameter Management
Controlling data in the BIM model is largely dependent on managing parameters. Make sure that all elements have the necessary parameters assigned to them and that they are filled in correctly at this point. For automated processes to run smoothly and without confusion or mistakes, parameter values must be consistent. Error reduction and improved accuracy can be achieved by automating parameter updates. You can support project analysis and decision-making with effective data extraction and reporting by keeping your parameters well-populated and organized.
6. Clash Detection and Resolution
Finding conflicts between various elements and systems in the model, such as MEP components crashing with structural elements, requires automated clash detection. Organize conflicts into categories and assign priorities by project requirements. After conflicts are identified, automatically generate reports for inspection and correction. Check that the model accurately incorporates resolved clashes to avoid recurrence. Frequent clash detection guarantees efficient construction workflows, lowering expensive on-site rework.
7. Drawing and Documentation Automation
Time can be saved and human error can be decreased by automating the production of construction drawings and project documentation. Determine that the views, sections, and schedules sheets are created by project requirements. Verify the positioning of the annotations, legends, and title blocks. Make sure that all drawings are up to date and in line with the most recent project information by automating the updating of drawing documentation as the model changes. This process increases document accuracy and speeds up the delivery of projects.
8. Data Export and Reporting
The process of exporting data for quantities, costs, and schedules can be made much simpler by automation. Verify that the information in the data exports matches that in the BIM model. This covers data integrity, formatting, and unit verification. To produce standardized and consistent outputs and guarantee that the data satisfies stakeholder or client requirements, automate the reporting process. Clear communication of project metrics is made possible by dependable data exports, which improves transparency and decision-making.
9. Model Coordination
Integrating different disciplines, like architecture, structure, and MEP, requires automated model coordination. To ensure that updates and revisions are correctly merged without causing conflicts, set up automated workflows to coordinate the models. Check that all disciplines are in alignment within the coordination space and run automated checks to ensure that modifications to one model do not adversely affect other models. To achieve a more seamless project execution, proper model coordination lowers the likelihood of design conflicts.
10. Project-Specific Requirements
Each project has specific needs that need to be taken into account when setting up the automation. Examine and adjust automation settings to meet the particular requirements of the project, including detailed modeling, particular compliance checks, or special client deliverables. Make sure automated procedures take these requirements into account and incorporate outside tools or scripts as necessary. The value of the BIM solution offered is increased when project-specific automation is well defined, supporting customized project outcomes and helping to meet client expectations.
Benefits of BIM Automation
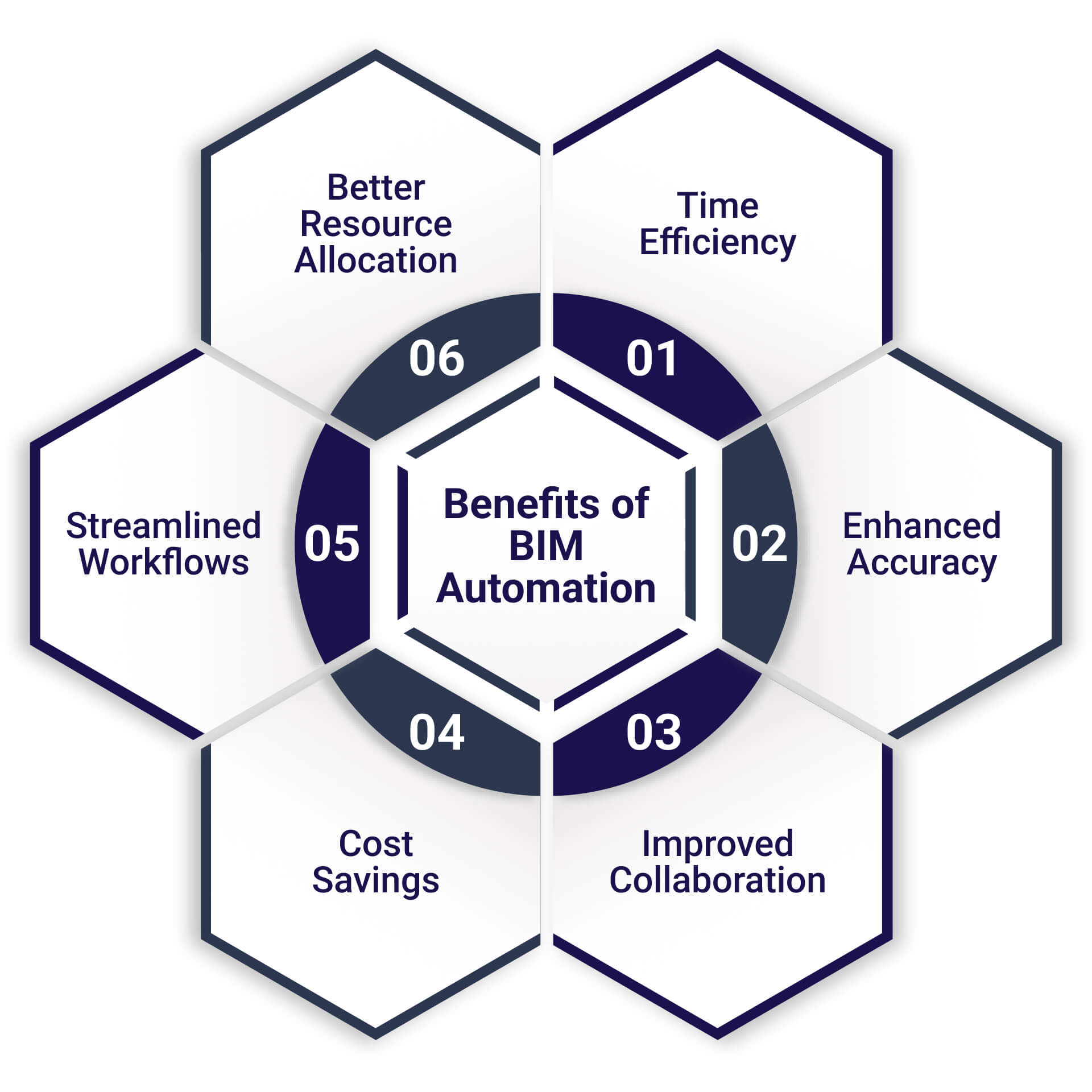
1. Time Efficiency
Complex or repetitive tasks take fewer hours to complete when BIM automation services are used. Processes like parameter updates, drawing generation, and clash detection are handled much more quickly by automated scripts than by human labor, freeing up time for analysis and design.
2. Enhanced Accuracy
By reducing the possibility of human error, automation enhances precision in clash detection, data management, and model coordination. Projects meet fewer delays and cost overruns when there are fewer errors.
3. Improved Collaboration
Real-time updates and data consistency are provided by BIM automation, which facilitates easier collaboration between various teams. The improvement of communication facilitates informed decision-making among those involved.
4. Cost Savings
BIM automation lowers project costs by reducing errors and manual labor. Budget overruns are avoided by using automated cost estimation and quantity take-offs, which provide accurate financial data.
5. Streamlined Workflows
Automation simplifies complex workflows, making it easier to manage large-scale projects. Automated processes like data extraction, clash management, and drawing generation ensure efficient project execution.
6. Better Resource Allocation
With automation handling repetitive tasks, team members can focus on strategic and creative aspects of the project, optimizing the use of human resources.
How BIM Automation is Implemented in Projects?
Scripting and Programming
Repetitive tasks in Revit or other BIM software can be automated by users with the help of automation applications, such as those written in Python or Dynamo. These scripts are specifically designed to fulfill the demands of particular projects, like parameter updates or the creation of complex geometry.
Using Third-Party Tools and Plugins
Advanced automation capabilities are provided by several plugins, such as the Revit add-ins and Navisworks for clash detection. These tools allow for advanced features like quantity extraction and automated drawing generation, and they integrate seamlessly with BIM software.
Integration with Other Systems
BIM-related software frequently works with project management or facility management tools through BIM automation. Automated processes for project tracking, scheduling, and facility maintenance are made possible by this integration.
Implementing Parametric Design
Users can create dynamic models that update automatically when improvements are made by using parametric design principles. For complex geometry or adaptable elements in architectural designs, this is essential.
Future Scope of BIM Automation
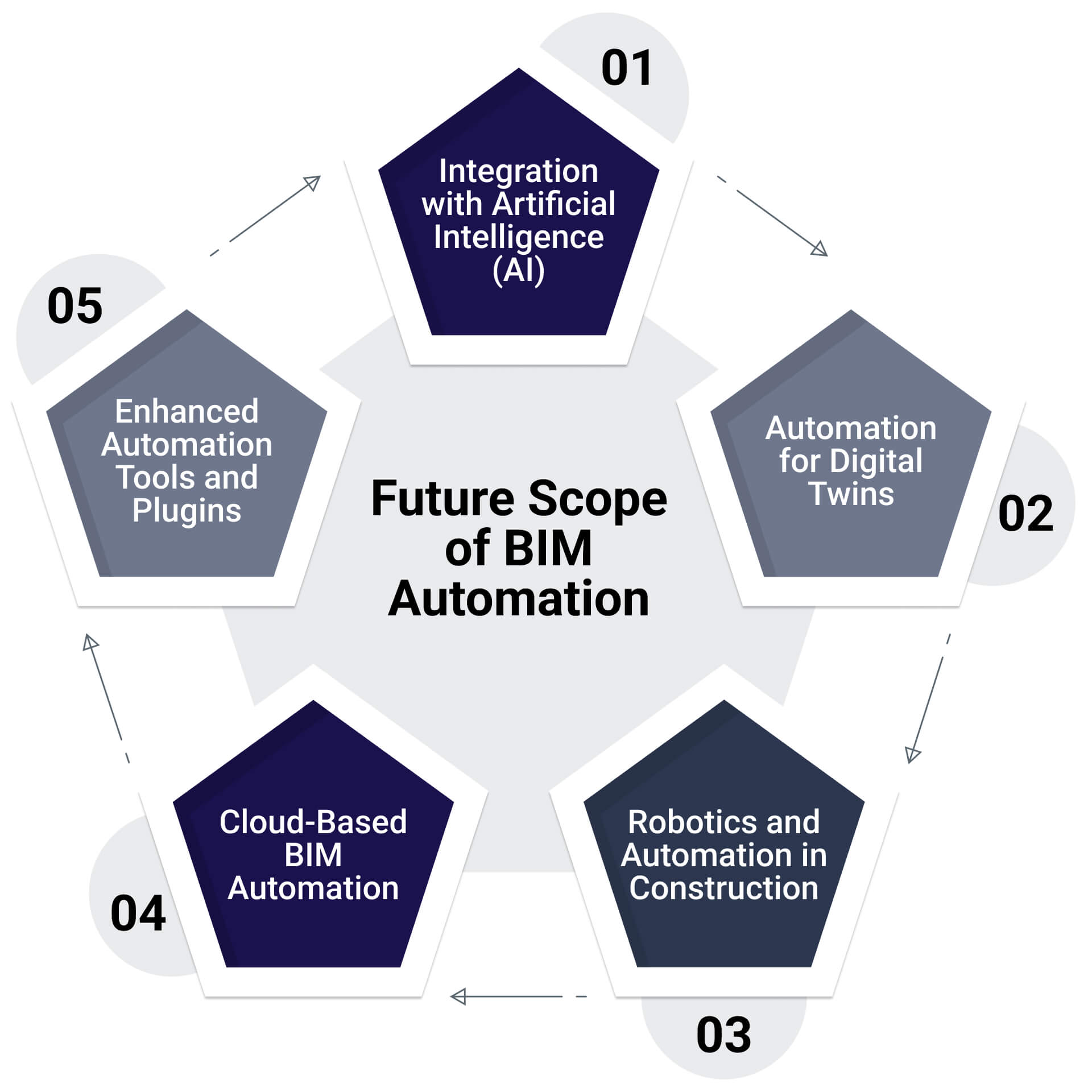
1. Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Combining AI and machine learning to automate difficult decision-making processes is where BIM automation is controlled. AI systems are capable of analyzing project data to forecast conflicts, optimize designs, and even make design recommendations.
2. Automation for Digital Twins
Digital twins are computer-generated images that incorporate real-time data to simulate actual buildings. Digital twin creation and management will be greatly simplified by BIM automation, which offers the most recent information on building performance and maintenance requirements.
3. Robotics and Automation in Construction
Automation will extend beyond software to the physical construction site, with robots and drones using BIM data for site inspections, material placement, and quality checks.
4. Cloud-Based BIM Automation
Cloud-based solutions will enable real-time collaboration and automation across global teams. With cloud computing, automated workflows can run 24/7, providing updates and insights as projects progress.
5. Enhanced Automation Tools and Plugins
As the demand for BIM automation grows, more sophisticated tools and plugins will emerge, offering greater flexibility and advanced features for all stages of construction, from design to facility management.
Conclusion
BIM automation is revolutionizing the AEC industry by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration. It streamlines workflows, reduces errors, and ensures projects are delivered on time and within budget. With advancements in AI, cloud computing, and robotics, BIM automation will continue to evolve, offering new possibilities for improving construction processes and project outcomes.
FAQs
What is BIM automation?
BIM automation involves using scripts, tools, and software to automate repetitive or complex tasks within a BIM environment, improving efficiency and accuracy in the design and construction process.
What are the main benefits of BIM automation?
The key benefits include time efficiency, enhanced accuracy, improved collaboration, cost savings, streamlined workflows, and better resource allocation.
Which tools are commonly used for BIM automation?
Common tools include Revit, Navisworks, Dynamo, and various third-party plugins and add-ins that offer automation capabilities.
How does BIM automation impact project costs?
BIM automation reduces manual work, minimizes errors, and provides accurate data for cost estimation, leading to significant cost savings.
What is the future of BIM automation?
The future of BIM automation will see integration with AI, digital twins, robotics, cloud-based solutions, and more advanced automation tools, enhancing its scope and applications in the AEC industry.
Can BIM automation be used for small-scale projects?
Yes, BIM automation is scalable and can be applied to small-scale projects to improve efficiency and reduce manual effort, making it a valuable tool regardless of project size.