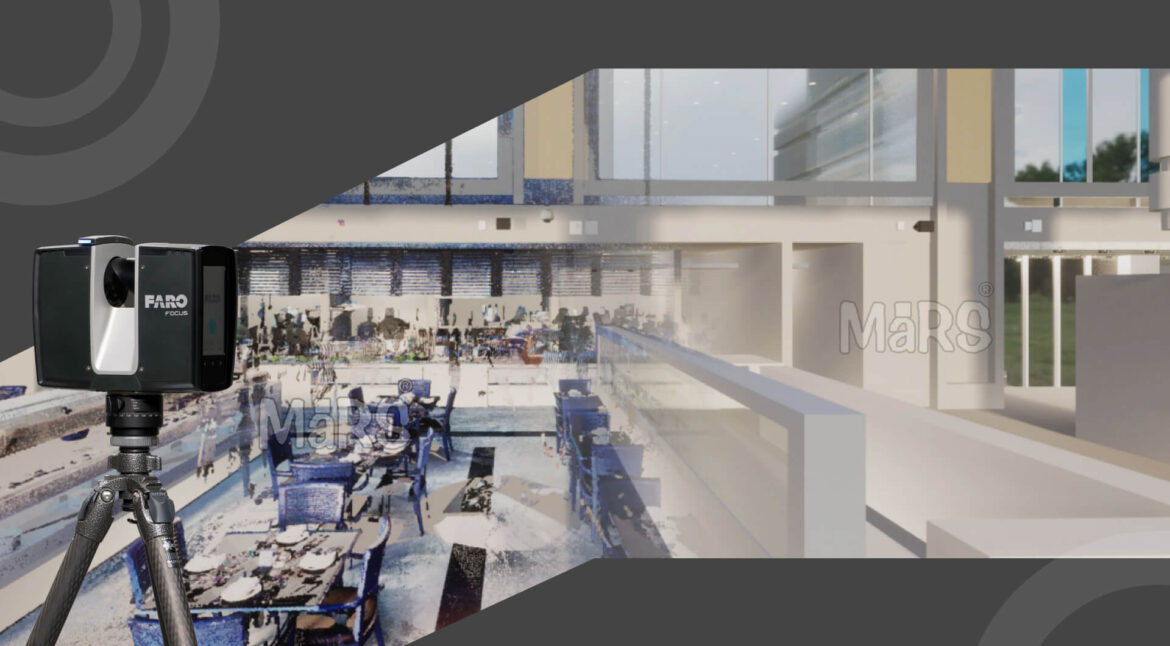
By generating exact digital models that capture each detail of existing structures, scanning has completely transformed the architecture and construction industries. This technology guarantees accuracy and efficiency throughout the entire planning, designing, and renovation process. To make the most of Scan to BIM services, it’s essential to follow a structured checklist and process that guides each phase of the project. Professionals can provide high-quality BIM models that fulfill project requirements and client expectations by following this process.
Scan to BIM Checklist

Pre-Scan Planning
Detail Pre-scan planning is the first step in the Scan to BIM process. This involves determining the right scanning technology, analyzing the project’s scope, and identifying the important areas for scanning. Planning reduces the need for reuse scans by guaranteeing that all relevant data is captured during the scanning process. Assuring that the completed BIM model meets all requirements involves working with stakeholders to set expectations and align the scan with project objectives.
Site Preparation and Safety
Setting up the area and making sure safety is essential before scanning starts. This involves removing any obstacles, protecting the area, and monitoring any risks that exist. Accurate collection of information is ensured and scanning error risk is reduced with proper site preparation. This is why scan to BIM services is essential. Safety protocols are implemented to protect personnel and equipment, and any necessary permits are obtained. This stage sets the foundation for an efficient scanning process and is useful for the collection of data.
Data Capture and Point Cloud Generation
Data capture is the core of the Scan to BIM process, where 3D laser scanners or other technologies are used to collect accurate measurements. A collection of millions of points that represent the scanned area in three dimensions is created from the information that was collected to create a point cloud model. To build thorough BIM models, accurate point cloud generation is crucial. As a result, this step is crucial to the process because the accuracy of the final model directly depends on the quality of the data.
Point Cloud Processing and BIM Modeling
After data capture, the point cloud is processed to remove noise and refine the data. This processed point cloud is then used to create a detailed BIM model. Along with geometric data, the BIM model includes details about systems, materials, and other construction elements. This model is a valuable resource for design, analysis, and project planning in the future because it functions as a digital twin of the current structure. The accuracy and stability of the BIM model are guaranteed by proper processing.
Quality Assurance and Verification
To guarantee accuracy and completeness, quality assurance (QA) and verification are crucial after the BIM model is created. In this step, the original point cloud data and the BIM model are compared, and additional checks are made against the actual site conditions. Any discrepancies are found and resolved. To guarantee that the model is a trustworthy resource for following project stages like design, construction, and facility management, quality assurance procedures (QA) help with confirming that the model accurately reflects the current structure.
Data Integration and Collaboration
The BIM model can be shared with stakeholders and integrated with other project data once it has been verified. Including additional information, like engineering specifications, architectural designs, or facility management data, is part of the scan to BIM process. To make sure that every team member has access to the latest model, efficient platforms and tools for collaboration are used. This step makes sure that everyone working on the project is using the same accurate information, improves decision-making, and lowers the possibility of conflicts.
Model Finalization and Documentation
The BIM model is modified to be ready for use in the project during its completion stage. This involves adding in any last-minute information, creating documentation that will be used for the duration of the project, and highlighting the model with relevant information. The completed model functions as a reliable resource for tasks related to building, remodeling, and maintenance. Ensuring that every relevant detail is recorded through proper documentation will help in the next stages of the project and guarantee consistency.
Ongoing Maintenance and Updates
Maintaining and updating the model requires constant work; scanning to BIM is not a one-time process. The BIM model needs to be updated so it can adjust for structural changes as they happen, such as improvements. The model will continue to be a useful tool for facility management and future projects if it is updated regularly. This step helps maintain the accuracy of the digital twin, ensuring it continues to provide relevant and reliable information over time.
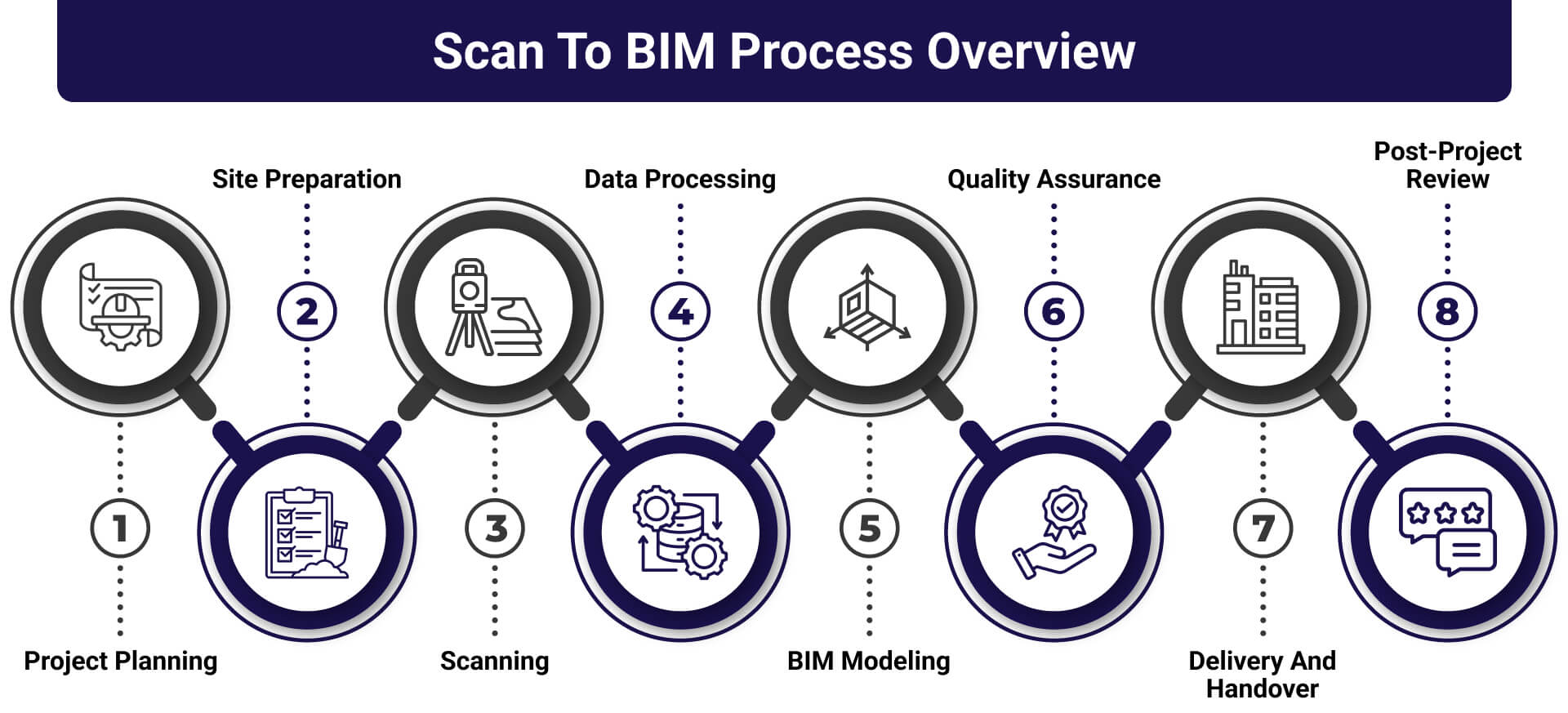
Scan to BIM Process Overview
1. Project Planning
Project planning is the first and most important step in the Scanning to BIM process. Set up the project’s goals, scope, and Level of Detail (LOD) to guarantee that everyone is aware of what is expected of it. Working together with stakeholders throughout this phase is crucial for setting expectations and coordinating the BIM model with the project’s goals. A successful project is largely dependent on careful planning, which also reduces risks and guarantees that the final BIM model fulfills all requirements.
2. Site Preparation
Getting access to the location and carrying out a complete site inspection is part of site preparation. The environment is prepared for scanning at this stage of the Scan to BIM services, with any barriers or difficulties detected in advance. Potential problems can be resolved early on in the scanning process, allowing for the precise and complete collection of data. A well-prepared site is necessary for both effective scanning and excellent BIM modeling.
3. Scanning
Scan to BIM revolves around the scanning phase, which involves using 3D laser scanning to collect accurate site data. To make sure that the point clouds produced are precise and inclusive, professionals at this stage verify the data quality in real-time. An accurate digital model of the structure is the result of accurate scanning.
4. Data Processing
A crucial part of the Point Cloud to BIM process is data processing, which creates and records the gathered Point Cloud data. To make sure the data is prepared for BIM modeling, this step includes organizing and improving it. Accurately processing the point clouds facilitates the seamless transition to BIM and allows for the production of accurate and in-depth models. A high-quality BIM model that satisfies project requirements requires efficient data processing
5. BIM Modeling
In this process, BIM modeling is where the magic happens. The processed point cloud data is imported into BIM software, such as Autodesk Revit, to create a detailed 3D model. This model represents the physical and functional characteristics of the building, including structural elements, systems, and materials. The BIM model is then verified against project specifications to ensure accuracy. Proper BIM modeling is essential for producing a reliable digital twin of the structure.
6. Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is a critical step in the Scan to BIM workflow. During this phase, the BIM model undergoes thorough reviews and checks to ensure it meets the defined standards and complies with project requirements. This includes verifying the accuracy of the data, checking for any discrepancies, and ensuring the model aligns with the project scope. Quality assurance ensures that the final deliverable is of the highest standard, reducing the risk of errors in the construction or renovation process.
7. Delivery and Handover
The final stage of the Scan to BIM process is the delivery and handover phase. The completed BIM model and all necessary files and documentation are given to the client. This stage guarantees that the client will receive an accurate and complete representation of their project. The BIM model’s features and functionalities, as well as how to use it for future maintenance and modifications, are all explained during the handover process. For the project to be successful overall and to satisfy the client, successful delivery and handover are essential.
8. Post-Project Review
The post-project review is the final step in the Scan to BIM process. This phase involves collecting feedback from the client and other stakeholders to assess the project’s success and identify any areas for improvement. The review also includes archiving project data for future reference and ensuring that all project deliverables have been met. Conducting a thorough post-project review helps in refining processes and enhancing the quality of future Scan to BIM projects.
Read Our Recent Blog: Scan to BIM vs Traditional Methods
Conclusion
To ensure accurate, dependable, and efficient results in any project, a comprehensive Scan to BIM checklist and process must be put into place. Stakeholders can guarantee the outstanding value of their Scan to BIM services by following the defined steps, which include pre-scanning preparation and post-project review. The systematic method of Scan to BIM helps experts generate complete digital models that improve decision-making, lower risks, and simplify workflows throughout the construction industry, whether for renovation of existing buildings, new construction, or facility management.
FAQs
What is the first step in the Scan to BIM process?
Arranging a site survey is the first stage of the Scanning to BIM process. To do this, a point cloud dataset for additional modeling is created by using 3D laser scanning technology to record the actual dimensions and features of the current building or structure.
What software is commonly used in the Scan to BIM process?
Commonly used software in the Scan to BIM process includes Autodesk Revit, AutoCAD, and Navisworks for BIM modeling, as well as point cloud processing tools like Leica Cyclone, Autodesk Recap, and Trimble RealWorks.
What challenges might arise during the Scan to BIM process?
Challenges during the Scan to BIM process can include difficulties in scanning hard-to-reach areas, managing large volumes of point cloud data, ensuring accuracy in complex geometries, and integrating the BIM model with existing project data.
What quality control measures are needed in the Scanning process?
Quality control measures in the Scanning process include validating the accuracy of the point cloud data, performing regular checks during the modeling process, comparing the BIM model against existing drawings or physical measurements, and conducting a final review before delivery.
What are the benefits of creating a Scan to BIM checklist?
Creating a Scan to BIM checklist ensures that all critical steps and considerations are addressed during the project. This improves accuracy, and consistency, and lowers the possibility of overlooking crucial tasks, all of which lead to a more seamless and effective project workflow.
What are the common mistakes to avoid in the Scan to BIM process?
Common mistakes to avoid in the Scan to BIM process include inadequate site preparation, poor equipment calibration, insufficient scan coverage, neglecting quality control measures, and failing to properly manage and organize point cloud data. These errors can lead to inaccuracies and increased project costs.
What role does documentation play in the Scan to BIM process?
Documentation is crucial in the Scan to BIM process as it records all steps, decisions, and data used during the project. This includes the scanning process, data management, modeling decisions, and quality control checks, providing a comprehensive record that supports future maintenance, renovations, and audits.
How does Scanning integrate with other BIM processes?
Scanning integrates with other BIM processes by providing the foundational as-built model that can be used in various stages of a project, including design, construction, and facility management. It ensures that all subsequent BIM activities are based on accurate and current data, facilitating better coordination and decision-making.